E-commerce SEO Secrets
By 2020, experts predict you’ll allocate almost half of your entire marketing budget for online content—and search engine marketing will take the lion’s share.
37.5 percent of your e-commerce consumer traffic already comes from online searches, and that number is steadily rising. Your online storefront needs to be SEO savvy to stand out from the growing crowd of online business.
So, you want to raise your search engine results page (SERP) ranking and catch consumer attention. Fine-tuning your e-commerce SEO will help you do that, and really, there’s nothing better.
Where do you start?
E-commerce SEO Secrets 1: Keywords Are More Important Than You Think.
E-commerce thrives because of search engines: Your consumers search what they’re looking for, and the search engine crawlers find it. How do they do that? Keywords.
If you want your e-commerce platform to rise above the competition, you’ll need to research your industry’s most frequently used keywords before you start a new content marketing campaign. (Note: Do this prior to rebranding your platform.)
Keywords come in different sizes. You must use multiple types to trigger a search engine’s crawlers.
- Head keywords: Simple, yet effective. These keywords drive high search volume and are quite competitive. Head keywords consist of one to two terms that highlight the specialty of your business or industry.
- Long-tail keywords: More specific, but higher-converting. These multiple-word keywords reflect potentially-exact search terms and are more likely to attract your target customers. They’re also less competitive, because they’re often hyper-specific or even branded.
Got that? Now here’s a little secret: it’s easiest to begin by creeping on your competition.
TIP #1—Start by Analyzing Amazon
No matter the size of your company, you’ll be competing with Amazon for consumer traffic. You can use Amazon’s search bar to identify different keywords that the site itself uses to draw in consumers.
Visit Amazon’s home page and enter a keyword or phrase that you think describes your product. Don’t click “Search.” Instead, look through the list of suggested searches Amazon provides for you.
Amazon’s search bar will provide you with samples of long-tail keywords that you can borrow. See our example search below, for toasters.

Note: this Amazon keyword tactic is mostly useful for selling products, not services.
TIP #2—Assess Competitors’ Keywords with SEMrush
A tool like SEMrush won’t identify new keywords for you, but it WILLl display the keywords your competition already uses.
Head to SEMrush’s website and find its search field. Type the name of a competitor into the field and click “Search.”
SEMrush will show you all the keywords your competitor has in use. The best part? You can borrow those keywords for your platform.
SEMrush will also show you a list of competitors comparable to the one you previously searched for, under its “competitors” tab, in case you’re not sure what companies share your market space.
Repeat the keyword research process through SEMrush until you’re satisfied with the number of head and long-tail keywords you’ve found. With a list of potential keywords at hand, you’ll need to narrow down your choices based on their value.
TIP #3—Cut Based on Search Volume
Assess the search volume of your keywords through Google’s Keyword Planner. Log into the platform and input your keyword of choice in the search bar.
You’ll find search volume in a column marked “Avg. Monthly Searches.”
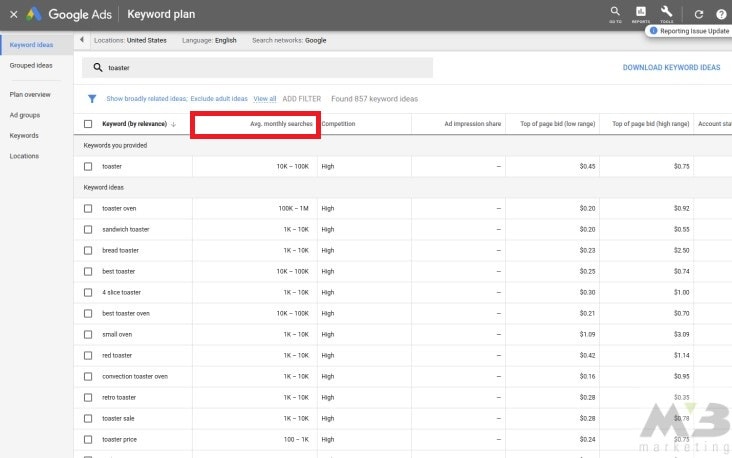
If your term is labeled “high volume,” it’s a frequently-searched term. HIGH VOLUME IS A GOOD THING, and you should consider using these for your own platform. If it’s labeled “low volume,” then it’s a less common term and won’t do your SEO efforts much good.
TIP #4—Check Your Bidding
Next to your keyword’s search volume, there should be a column on Google Keyword Planner labeled “Competition.”
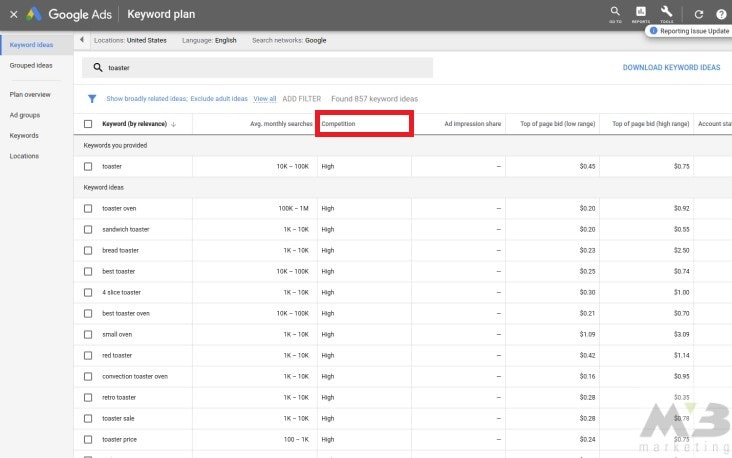
This column shows how many people are “bidding” on your keyword of choice. “Bidding” describes the process of utilizing a keyword to make money. If Google Keyword Planner notes that your keyword’s bid is high or average, then it’s a term worth using. Low bids reflect lesser use among your competition.
TIP #5—Assess Keyword Difficulty
SEMrush also helps you assess your keyword’s difficulty. This metric will determine whether your keyword of choice will boost your content to the first page of a search engine.
It’s easy to have SEMrush find your keyword’s difficulty. Using the platform, research a keyword as you normally would. Then, on the left sidebar, find “keyword difficulty.”
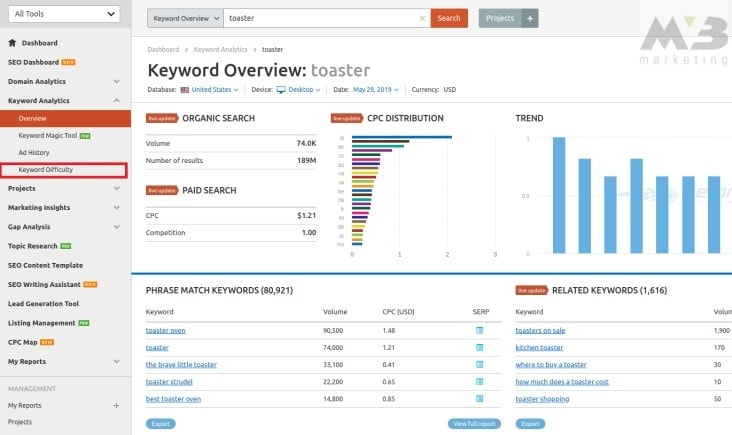
Find the “difficulty %” column. Higher numbers here indicate it’s more difficult for content to rank on the first page of SERPs using the keyword. Lower numbers, alternatively, mean that it’s easier for content with that term to boost its SERP ranking.
E-commerce SEO Secrets 2: Unique Content is King
Keywords aren’t the only essential SEO element you need to integrate into your platform. To boost your SERP ranking, your content must be unique to catch the eye of a search engine crawler.
Just as importantly, your content must be information-rich. Length comes into play here; the average length of a first page SERP result is roughly 1,800 words. Length doesn’t dictate value, however.
Instead, when creating content, make sure you’re answering consumers’ questions or creating content they can revisit at a later date. Some of the best content to create includes:
E-commerce SEO Secrets 3: Use Schemas to Stabilize Your Site
Brand individuality should be visible in your platform snippet, another place for strong e-commerce SEO. Snippets quickly deliver information about your storefront’s products, operations, and demographic to Google crawlers, making those few characters exceptionally important.
The best way to build up your business’ reputation with crawlers, then, is to create an information-rich snippet to entice consumers.
You can build these informative elements into your snippet via schemas. A schema is a CSS term that you integrate into your content to better translate what you’ve written into a language that crawlers can speak. The more diverse and accurate your schemas are, the better your content snippets will be. With stronger snippets comes a stronger SERP ranking.
You can build schemas through a program such as Google Markup. Google Markup will offer you a variety of schema terms to consider. Once you’ve found the one you like, you can click on it, and Markup will do your coding for you.
Next once the process is complete, you can copy and paste your content into your original platform, or download it. You’re finished, give your code a test in a structured data testing tool.
If you’re using WordPress to house your platform, the site’s many plugins will do the same work as Google Markups. WordPress’s schema plugins include.
Not all e-commerce SEO is content SEO. You’ll need to work with Technical SEO to optimize your platform and prevent data lapses that could undercut your credibility as a business.
E-commerce SEO Secrets 4: Who Said Audits Couldn’t Be Fun?
SEO audits help identify potential e-commerce platform mishaps. When you run an SEO audit you can better ensure that your site has a watertight architecture that stands out to Google’s crawlers.
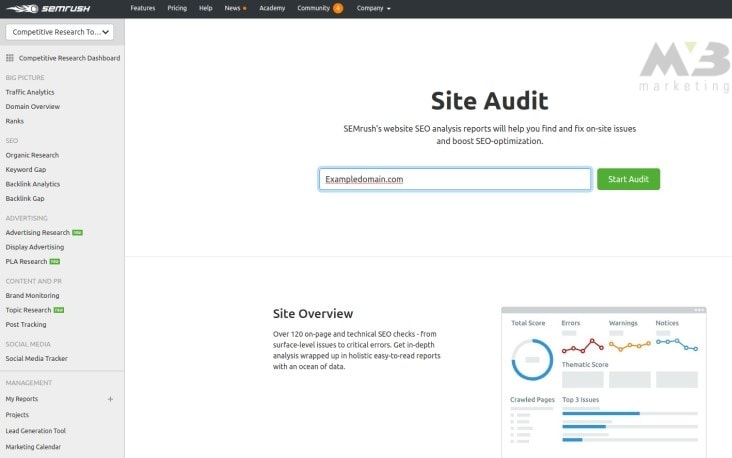
To run a site audit with SEMrush:
1. Create a project on the platform dashboard
2. Enter a Project Name
3. Click “Site Audit”4. Change the “default” parameter “limit of checked pages” so all your pages can be assessed
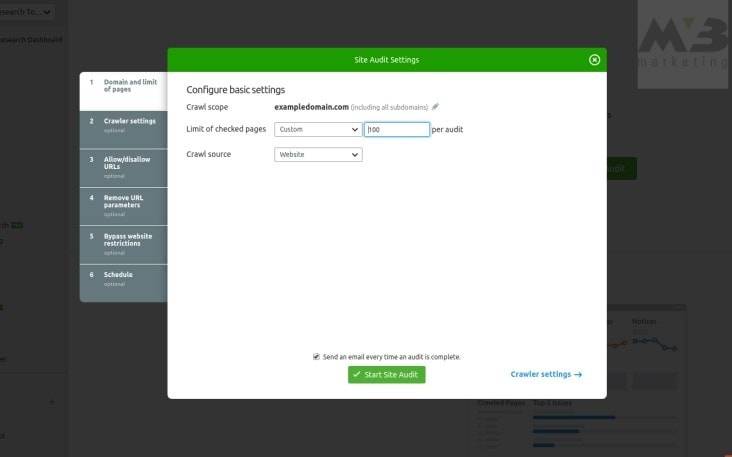
Then, SEMrush will generate your site health based on the number of checks passed and failed. It’ll present you with this information in the form of a bar.
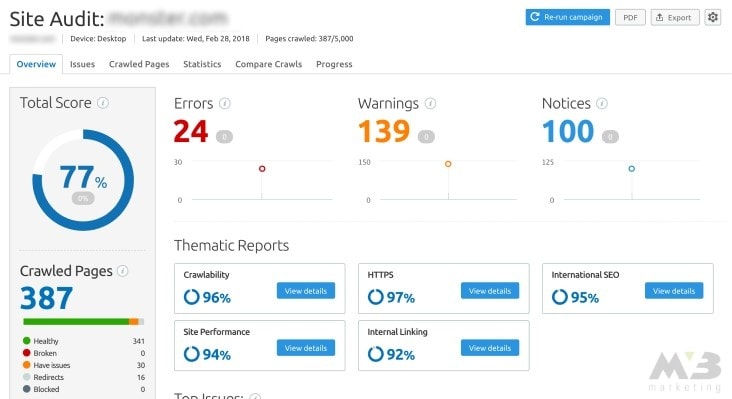
The green portion of the bar reflects pages that are “healthy” or effective. Orange-marked pages have issues, and red pages are broken entirely. SEMrush will also provide you with a list of the most crucial errors for you to take care of immediately.
Common site errors include:
- Duplicate pages
- Lost meta descriptions
- Broken links
Remove Your Duplicate Pages
You’re most likely to duplicate content when improving your platform’s mobile compatibility. If you use different URLs for your canonical and mobile content, you may have forgotten to distinguish between the two.
Based on the information SEMrush or a similar tool provides, you need to remove duplicate content from your website. You can do this in several ways.
- rel=canonical: Use this HTML tag on the page you want Google to index. When you do, it’ll ignore the duplicate pages in favor of the “canonical page.”
- 301 redirect: Many WordPress plugins allow you to redirect the audience attention from a duplicate page to a canonical page.
- Passive parameters: You can also let Google know that one of your duplicate pages is “passive” by diving into Google’s Search Console and adjusting URL search parameters.
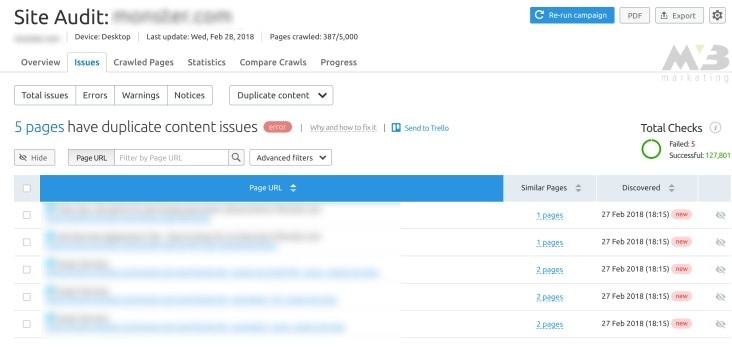
Click “Add parameter” and enter the URL of the duplicate page, selecting “No: doesn’t affect page content.”
Once you click “Save,” your duplicate content will no longer register with Google’s crawlers.
Remove Dead Links
When you restructure your platform, links can fall by the wayside. Content that gets deleted or replaced can leave dead links in its wake.
If you have dead links on your website, you can use Google’s Search Console to identify those lost links and re-affiliate them with live content.
1. Log into your Google account
2. Through Google Search Console, click on “Crawl Errors,” under the diagnostics tag
3. Click “Not Found”
With that, you’ve found the dead links and mobile 404s on your platform. You need to then edit those links manually using ctrl+k or the control panel, accessed via your right mousepad.
Rewrite Lost Meta Descriptions and Tags
Similarly, you can lose your meta descriptions and title tags when restructuring your platform or updating your content.
You have the opportunity to craft your meta descriptions, title tags, and other SERP content for your platform. If SEMrush tells you that you have missing meta descriptions, you’ll need to replace them.
You can code in a meta description like so:
<meta name=”description” content=” Your Page Description Goes Here.”/>
E-commerce SEO Secrets 5: Gotta Go Mobile
Mobility is the name of the game in e-commerce. Mobile e-commerce makes up 34.5 percent of all e-commerce sales. If your platform can’t be accessed via phone or tablet, you’re failing to reach a significant chunk of your audience.
To continue increasing your e-commerce SEO, check your site’s mobile compatibility with Google’s mobile-friendly checker tool.
Enter your URL into the tool’s search bar. After you’ve clicked “Test URL,” Google will display your site’s mobile usability in clear terms. It’ll either state that no usability errors were detected or outline the site elements that your average phone won’t be able to process.
See the tutorial on Technical SEO for descriptions of how you can make your platform more mobile compatible.
E-commerce SEO Secrets 6: Network, Network, Network
Finally, you’ll need to network among your e-commerce peers to build a strong SEO link network for your platform. E-commerce backlink networks establish your business’ authority, and with greater authority comes a higher SERP ranking.
Your site will still need internal links or links that lead to your pages. However, real e-commerce SEO value and platform authority come from your external links.
Here are a few different ways to find authoritative external links.
Use Your Competitor’s Research
Much like with your keyword usage, the best place to start your link research is on your peers’ platforms. Read the content your peers produce and identify the hyperlinks they’ve interwoven with their work.
The most authoritative external links include:
- .gov, .org, .edu platforms
- Well-established corporate sites
- Research studies and PDFs
- Nationally and internationally respected newspapers
Use Relevant Links
You don’t want to grab external links without thought. The links you use to support your content should be immediately relevant to the conversation you’re holding with your audience.
You should also avoid using outdated sources as external links. The oldest links on your page should be a year old, maybe two. If you’re posting new content in 2019 and using sources from 2002, your content won’t register with search engine crawlers as relevant.
Integrate Keywords with Your Anchor Text
To bring things full circle, you should use head keywords and long-tail keywords as anchor text for the external links you build into your content. When you do so, you create an SEO double-whammy. You also prove the relevance of your links to crawlers, as well as to your audience.
All of the benefits, none of the work? Boost your E-Commerce SEO today with MV3.
Do you want to optimize your e-commerce SEO and maximize your sales—without doing all that hard work? Hire the MV3 team.
We’re here to help you discover consumer-oriented keywords, improve your site’s speed and structure, and find the consumers that will escalate your business. Contact us today.
Conclusion
Is your company in need of help? MV3 Marketing Agency has numerous Marketing experts ready to assist you. Contact MV3 Marketing to jump-start your business.


